Are you considering investing in a portfolio of high-quality commercial properties without the need for substantial capital or the hassle of property management? Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) provide an accessible way to invest in the booming real estate market, making wealth growth easier than ever. Let’s explore the key aspects of REITs in this blog.
What is a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT)?
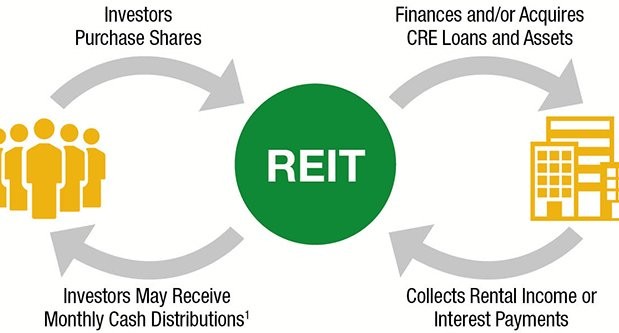
A Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) is a company that owns, operates, or finances income-generating real estate. Typically structured as corporations, these trusts manage portfolios of high-value properties and mortgages. REITs lease properties and collect rent, which is subsequently distributed among shareholders as income and dividends.
Investors can participate in the real estate market and earn dividend income, allowing for capital appreciation without direct property ownership. REITs can include various types of properties, such as data centers, healthcare facilities, and apartment complexes.
Types of REITs
REITs can be classified in several ways:
1. Based on the Nature of the Real Estate Asset
- Equity REITs: These REITs own and operate income-producing properties, like offices and warehouses. Their primary revenue comes from rent. As of Q1 2024, the estimated value of the U.S. equity REIT market was $3.9 trillion, according to NAREIT (National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts).
- Mortgage REITs: These focus on providing financing to real estate owners through mortgages and mortgage-backed securities, earning income from the interest on these loans.
- Hybrid REITs: A combination of equity and mortgage REITs, these own properties and hold mortgages.
2. Based on the Nature of Trading
- Publicly Traded REITs: Registered with the SEC and listed on stock exchanges, their shares can be bought and sold like stocks. Prices are influenced by market dynamics and the performance of underlying real estate assets.
- Public Non-Traded REITs: Not listed on public exchanges, these shares are sold through brokers and are less liquid.
- Private REITs: These are not registered with public exchanges and are typically offered through private placements to institutional investors or high-net-worth individuals.
Top REITs in India
The Indian REIT market is relatively new, but it has gained traction. Here are some of the leading REITs:
- Embassy Office Parks REIT: India’s first publicly listed REIT, focusing on office spaces across major cities.
- Mindspace Business Parks REIT: Invests in commercial properties in cities like Mumbai and Hyderabad.
- Brookfield India Real Estate Trust REIT: Concentrates on commercial office spaces in key business hubs.
- India Grid Trust (IndiGrid): An Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) that focuses on power transmission assets.
- PowerGrid Infrastructure Investment Trust (PGInvIT): Another InvIT focusing on energy transmission infrastructure.
What is REIT Investing?
REIT investing involves purchasing shares in a REIT company that manages income-generating real estate. Key points include:
- Structure: REITs pool capital from multiple investors to acquire and manage real estate assets like office buildings and shopping malls.
- Income: They earn revenue through rent or interest from real estate loans, distributing most income to shareholders as dividends.
- Liquidity: Publicly traded REITs allow for easy buying and selling on stock exchanges.
- Diversification: Investing in REITs provides exposure to a diversified portfolio of properties without the challenges of direct ownership.
- Tax Benefits: In many jurisdictions, REITs enjoy tax exemptions if they distribute a significant portion of their income to shareholders.
How to Invest in REITs in India
Investing in REITs involves a straightforward process:
Step 1: Explore Your Options
Identify the type of REIT that aligns with your investment goals.
Step 2: Choose Your Investment Vehicle
You can invest in:
- Individual REIT Stocks: Target specific properties for potentially higher returns (requires more research).
- REIT Mutual Funds: Pool money with other investors to buy shares in multiple REITs, providing diversification and lower risk.
- REIT ETFs: Similar to mutual funds but trade like stocks, offering flexibility.
Step 3: Open an Investment Account
Set up an account with a reputable brokerage.
Step 4: Conduct Your Research
Evaluate the REIT’s track record, fees, and the current market conditions.
Step 5: Diversify and Monitor
Invest in various REITs and regularly review your portfolio.
Limitations of REITs
While REITs offer numerous benefits, they also come with limitations:
- Market Risk: REIT values can fluctuate based on real estate market conditions and economic factors.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: Rising interest rates can negatively impact REIT values.
- Limited Control: Investors have little say in the management of properties owned by the REIT.
- Management Fees: Fees can reduce overall returns.
- Concentration Risk: Some REITs may focus heavily on specific regions or property types, increasing risk if those areas face challenges.
Conclusion
Real Estate Investment Trusts provide a unique opportunity to access the real estate market without the complexities of direct ownership. With various types of REITs catering to different sectors, they offer diversification, steady income, and liquidity. However, potential investors must also consider the limitations, including market volatility and regulatory risks. Understanding how to invest and weighing the pros and cons is crucial for making informed decisions in this growing sector.
Leave a Reply